How To Load Program For At89c51snd2c

Request Atmel AT89C51-24PI: IC MICRO CTRL 24MHZ 40DIP online from Elcodis, view and download AT89C51-24PI pdf datasheet, Embedded - Microcontrollers specifications. Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conven. Tional nonvolatile memory programmer. By combining a. The load address dem and programmer monitor the phone line for incoming field contains the address at which the data is to be writ- calls. Page 5 Microcontroller It is important to note that invalid packets are NEVER pro- Switch settings: grammed into the application controller. Download opera mini for windows 10. To do so would require that the program memory in the controller. Load or unload a template or add-in program. Load templates or add-ins. Unload templates or add-ins. Make a template or add-in available whenever you start Word. Load templates or add-ins. When you load a template or add-in, it remains loaded for the current Word session only. If you quit and then restart Word, the template or add-in is not.
I have a USB to Serial breakout which has CP2102 and MAX232 chips on it. I wrote a program in Keil and generated the Hex File. How do I flash this hex file onto the AT89C51 (which is also another board with all the capacitors,resistors and crystal oscillator, everything is there) using the USB to Serial breakout? Flash Magic works only for philips chips, what is the alternative to ATmel chips?
1 Answer
$begingroup$The AT89C51 chip should contain an embedded USB boot loader pre-loaded on the chip. The boot loader is used to program the flash. The USB Boot-loader is described in this document.
The USB Boot-Loader works with the Atmel FLIP software. The FLIP software is available for free from the Atmel website.
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged atmel8051max232cp2102hex-file or ask your own question.
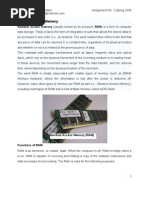
 Permalink
PermalinkLoad Program From Disc
Join GitHub today
GitHub is home to over 40 million developers working together to host and review code, manage projects, and build software together.
Sign up| .TH DFU-PROGRAMMER 1 'May 28, 2014' 'DFU-PROGRAMMER' ' |
| .SH NAME |
| dfu-programmer - USB firmware upgrading for Atmel microcontrollers |
| .nh |
| .SH SYNOPSIS |
| .Bdfu-programmer |
| target[:usb-bus,usb-addr] command [options] [parameters] |
| .br |
| .Bdfu-programmer |
| --help |
| .br |
| .Bdfu-programmer |
| --targets |
| .br |
| .Bdfu-programmer |
| --version |
| .SH DESCRIPTION |
| .Bdfu-programmer |
| is a multi-platform command line Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU) based programmer |
| for the flash memory on Atmel AVR, AVR32, XMEGA and 8051 based microcontrollers |
| which ship with a USB boot loader. |
| It supports In System Programming (ISP) for developers and potentially |
| product updates in the field. |
| Those boot loaders are patterned after the standard USB DFU 1.0 class |
| specification, but depend on extensions defined by Atmel to the extent |
| that standard DFU drivers will not work. |
| .PP |
| To use it, first connect the device to be programmed and ensure that it |
| comes up in DFU mode. |
| The microcontrollers come up in that mode as shipped by Atmel; |
| or they may reenter that mode after a special hardware reset. |
| Then invoke this program to issue one or more DFU commands. |
| You will normally need to start by issuing the 'erase' command; |
| the default security policies prevent extracting firmware, to prevent |
| reverse engineering of what is usually proprietary code. |
| .SH SUPPORTED MICROCONTROLLERS |
| These chip names are used as the command line 'target' parameter. |
| .IP'8051 based controllers:' |
| at89c51snd1c, at89c51snd2c, at89c5130, at89c5131, |
| at89c5132 |
| .IP'AVR based controllers:' |
| at90usb1287, at90usb1286, at90usb1287-4k, at90usb1286-4k, |
| at90usb647, at90usb646, at90usb162, at90usb82, |
| atmega32u6, atmega32u4, atmega32u2, atmega16u4, |
| atmega16u2, atmega8u2 |
| .IP'AVR32 based controllers:' |
| at32uc3a0128, at32uc3a1128, at32uc3a0256, at32uc3a1256, |
| at32uc3a0512, at32uc3a1512, at32uc3a0512es, at32uc3a1512es, |
| at32uc3a364, at32uc3a364s, at32uc3a3128, at32uc3a3128s, |
| at32uc3a3256, at32uc3a3256s, at32uc3a4256s, at32uc3b064, |
| at32uc3b164, at32uc3b0128, at32uc3b1128, at32uc3b0256, |
| at32uc3b1256, at32uc3b0256es, at32uc3b1256es, at32uc3b0512, |
| at32uc3b1512, at32uc3c064, at32uc3c0128, at32uc3c0256, |
| at32uc3c0512, at32uc3c164, at32uc3c1128, at32uc3c1256, |
| at32uc3c1512, at32uc3c264, at32uc3c2128, at32uc3c2256, |
| at32uc3c2512 |
| .IP'XMEGA based controllers:' |
| atxmega64a1u, atxmega128a1u, atxmega64a3u, atxmega128a3u, |
| atxmega192a3u, atxmega256a3u, atxmega16a4u, atxmega32a4u, |
| atxmega64a4u, atxmega128a4u, atxmega256a3bu, atxmega64b1, |
| atxmega128b1, atxmega64b3, atxmega128b3, atxmega64c3, |
| atxmega128c3, atxmega256c3, atxmega384c3, atxmega16c4, |
| atxmega32c4 |
| .IP'STM32F4 controllers (experimental):' |
| stm32f4_B, stm32f4_C, stm32f4_E, stm32f4_G |
| .SH USAGE |
| There are no mechanisms to implement gang programming. |
| By default, the first device that matches the id codes for the |
| given target is selected. Many targets share the same id codes. |
| Accordingly, you will usually avoid connecting more than one |
| device of a given family (AVR, XMEGA, AVR32 or 8051) at a time. |
| .PP |
| The target may be qualified with the USB bus and address number |
| of the device you wish to program. This allows programming multiple |
| devices of the same family at the same time. |
| .PP |
| All of these commands support the 'global options'. |
| Unless you override it, |
| commands which write to the microcontroller will perform |
| a validation step that rereads the data which was written, |
| compares it to the expected result, and reports any errors. |
| .PP |
| Note that unlike Atmel's BatchISP program, dfu-programmer will |
| only perform a single operation at a time. Erasing and programming |
| require separate commands. |
| .HP |
| .Bconfigure |
| register |
| [--suppress-validation] |
| data |
| .br |
| Bootloaders for 8051 based controllers support writing certain |
| configuration bytes. |
| .HP |
| .Bdump |
| [--force] |
| [--bin] |
| [(flash) --user --eeprom] |
| .br |
| Reads the program memory in flash and output non-blank pages in ihex format |
| to stdout. Use --force to output the entire memory and --bin for binary |
| output. User page and eeprom are selected using --user and --eeprom. |
| .HP |
| .Berase |
| [--force] |
| .br |
| Erases all the flash memory. For AT90 and ATmega type devices a |
| chip erase must be performed before other commands become available. |
| Erase first checks if the memory is blank unless --force flag is set. |
| .HP |
| .Bflash |
| [--force] |
| [(flash) --user --eeprom] |
| [--suppress-validation] |
| [--suppress-bootloader-mem] |
| [--serial=hexbytes:offset] |
| file or STDIN |
| .br |
| Writes flash memory. The input file (or stdin) must use the 'ihex' file |
| format convention for a memory image. --suppress-bootloader-mem |
| ignores any data written to the bootloader memory space when flashing |
| the device. This option is particularly useful for the AVR32 chips. |
| The --force flag tells the program to ignore whether memory inside |
| the program region is blank. |
| User page and eeprom are selected using --user and --eeprom. |
| The user space flash on AVR32 chips lies outside of the normal range |
| of flash blocks and is designed to contain configuration parameters. |
| Bootloader configuration uses the last 4 to 8 bytes of the user page. |
| If this data is corrupted, the device will restart into the |
| bootloader until valid data is used (see atmel doc7745 or doc32166). |
| --force is always required here. |
| .PP |
| --serial provides a way to inject a serial number or other unique |
| sequence of bytes into the memory image programmed into the |
| device. This allows using a single .ihex file to program multiple |
| devices, and still give each device its own unique serial number. For |
| example, --serial=ABCDEF01:0x6000 would program the byte at 0x6000 |
| with the hex value AB, the byte at 0x6001 with the value CD, and so |
| on. There must be an even number of hex digits, but the sequence can |
| be any length. The offset is assumed to be given in hex if it starts |
| with a '0x' prefix, octal if it begins with a '0', otherwise is it |
| assumed to be decimal. |
| .HP |
| .Bsetsecure |
| .br |
| Sets the security bit on AVR32 chips. This prevents the content being |
| read back from the chip, except in the same session in which it was |
| programmed. When the security fuse is set, almost nothing will work |
| without first executing the erase command. The only way to clear the |
| security fuse once set is to use a JTAG chip erase, which will also |
| erase the bootloader. |
| .HP |
| .Bget |
| register |
| .br |
| Displays various product identifier bytes. |
| .HP |
| .Blaunch |
| [--no-reset] |
| .br |
| Launch the application by resetting the device. The --no-reset flag |
| can be used to launch the device without a reset (jump to the start |
| address of the program). |
| .SS Global Options |
| --quiet - minimizes the output |
| --debug level - enables verbose output at the specified level |
| .SS Configure Registers |
| The standard bootloader for 8051 based chips supports writing |
| data bytes which are not relevant for the AVR based chips. |
| .LP |
| BSB - boot status byte |
| .br |
| SBV - software boot vector |
| .br |
| SSB - software security byte |
| .br |
| EB - extra byte |
| .br |
| HSB - hardware security byte |
| .SS Get Register |
| bootloader-version - currently flashed bootloader version |
| .br |
| ID1 - device boot identification 1 |
| .br |
| ID2 - device boot identification 2 |
| .br |
| manufacturer - the hardware manufacturer code |
| .br |
| family - the product family code |
| .br |
| product-name - the product name |
| .br |
| product-revision - the product revision |
| .br |
| HSB - same as the configure_register version |
| .br |
| BSB - same as the configure_register version |
| .br |
| SBV - same as the configure_register version |
| .br |
| SSB - same as the configure_register version |
| .br |
| EB - same as the configure_register version |
| .SH BUGS |
| None known. |
| .SH KNOWN ISSUES |
| The at90usb series chips do not make available any read/write protect |
| flags so the |
| .Bdump |
| or |
| .Bflash |
| command may fail with a less than helpful error message. |
| .PP |
| To remove |
| .Bany |
| write or read protection from any chips, a full chip erasure is required. |
| For AVR32 chips an erase operation over USB will remove protection until the |
| device is rebooted. To remove the protection more permanently requires a |
| JTAG erase (which will also erase the bootloader). |
| .PP |
| You may need to be a member of the |
| .Buucp |
| group in order to have access to the device without needing to be root. |
| .SH AUTHOR |
| Weston Schmidt <weston_schmidt@alumni.purdue.edu> |
| .SH SEE ALSO |
| .UR dfu-programmer.sourceforge.net |
| http://dfu-programmer.sourceforge.net |
| .UR USB DFU Bootloader Datasheet (8052, AVR) |
| http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc7618.pdf |
| .UR AVR32 UC3 USB DFU Bootloader Protocol |
| http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc32131.pdf |
| .UR FLIP USB DFU Protocol |
| http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc8457.pdf |
| .UR AVR32 UC3 USB DFU Bootloader |
| http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc7745.pdf |
| .SH COPYRIGHT |
| Copyright (C) 2005-2015 Weston Schmidt |
| This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify |
| it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by |
| the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or |
| (at your option) any later version. |
| This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, |
| but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of |
| MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the |
| GNU General Public License for more details. |
| You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License |
| along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software |
| Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301, USA |
Copy lines Copy permalink